SEBI regulates the mutual funds industry in India in the finance sector. The regulation would provide investor interest, transparency, and moral concerns. To make wise investments at VSRK Capital, how the mutual fund industry in India is regulated by SEBI and how SEBI regulates the industry’s operations.
Regulation of Funds by SEBI
-
- Who regulates the mutual funds in India? Mainly SEBI. Mutual funds operating in India are governed by SEBI, the Securities and Exchange Board of India, by making regulations, ensuring their compliance, transparency, and fulfilling their functions to safeguard investors and maintain market integrity.
- Indian mutual fund industry under SEBI is regulated by a robust supervisory structure, which manages the registration of funds, day-to-day affairs, investor disclosures, and compliance for maintaining transparency, fairness, and investor protection.
- SEBI sees to it that on a continuous basis, as per regulation, retail investor interests are guarded via disclosure, transparency, ethics, and risk disclosures, along with the MF houses acting with fairness in behavior and proper management of their funds.
Why is SEBI Regulation Important?
-
- SEBI’s culture ensures that those who regulate India’s mutual funds align with global best practices.
- SEBI governs the mutual fund sector in India to ensure ethical investment practices.
- Regulatory vigilance brings confidence to investors, reduces risk, and enhances transparency.
Registration & Approval Process
-
- At the starting time of this artificial industry, SEBI has made it mandatory for all Asset Management Companies (AMCs) to be registered.
- SEBI governs the mutual fund sector in India and examines material, track record, and compliance standards.
- It ensures AMCs comply with capital requirements, segregation of funds, and appointment of trustees.
SEBI’s Key Regulations
Disclosure Norms
-
- SEBI requires regular disclosure of portfolio statements, NAVs, and performances of the scheme to keep investors informed and shielded from malpractices or misleading schemes.
- SEBI places the Indian mutual fund industry under a uniform set of disclosure mechanisms by laying down disclosures, audit norms, and report presentation, which instills confidence in the investors and maintains market integrity.
- SEBI mandates that mutual fund schemes reveal their daily NAV, asset allocation, and risks, thereby providing an opportunity to the investor to make well-informed decisions in following up on the performance of their investments periodically.
Regulator of Mutual Funds in India
Asset Allocation Norms
-
- For better investor protection, SEBI sets specific limits on the extent to which mutual funds can invest in different asset classes such as equity, debt, and derivatives to promote prudent and balanced portfolio investment.
- By limiting exposure, SEBI prevents the Indian mutual fund industry from becoming over-concentrated proprietors of highly risky instruments, reducing systemic risks, and protecting them from aggressive risk-taking or fund strategies.
- SEBI mandates that fund managers have to follow diversification guidelines based on the fund’s objective to reduce risks and ensure the investments are least in agreement with the announced fund strategy and investor intentions.
Expense Capping
In the interest of the investor, SEBI mandates capping of fund management and administration charges to enable mutual funds to be within reach and houses not to charge too high a price for their services.
Such regulatory discipline provides assurance that the Indian mutual fund industry does not lie to investors, either in the form of unscrupulous or disproportionate fees, making mutual funds accessible and transparent as regards all mutual fund schemes.
SEBI makes sure that, because of cost regulation, mutual fund fees are transparently disclosed, are reasonably consistent, are “correct” fees, and are free of exploitative charges that would severely reduce investors’ long-term returns.
Investor Protection
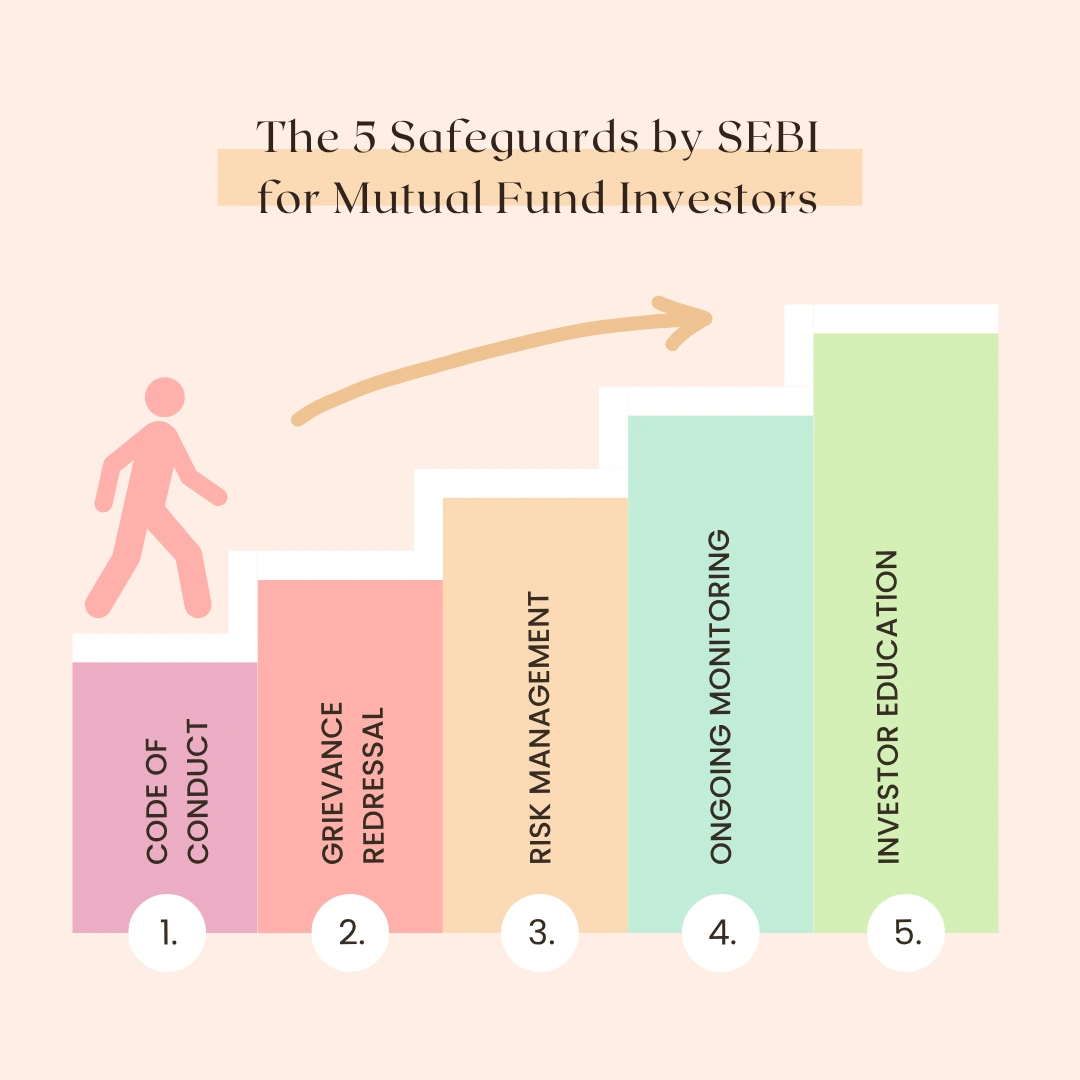
Code of Conduct
-
- SEBI enforces ethical norms being adhered to by AMCs, trustees, and distributors.
- It pertains to day-to-day behavior.
- It ensures fair treatment, avoids mis-selling, and encourages integrity.
Redressal Mechanism
-
- SEBI offers investor empowerment in the form of arbitration cells and the SCORES portal.
- The mutual fund industry working in India is regulated by SEBI to address complaints in a time-bound process.
- Will enhance trust and reliability across the investor ecosystem.
Risk Management Procedures
-
- SEBI mandates AMCs to implement disaster recovery arrangements that are sufficient.
- As mutual fund governance under Indian laws is ensured by SEBI, which shall minimize cyber, operational, and procedural risk.
- Ensures schemes are stress tested and liquidity is reserved.
Continuing Monitoring & Compliance
-
- SEBI tracks periodic audit, mystery shopping, and compliance.
- Again, whoever is in charge of Mutual Fund India needs on-site audits and verification of data.
- The Mutual Fund Industry in India is Regulated by SEBI to levy penalty for default shall safeguard all investor interests.
Investor Education Programmes
-
- SEBI implements programs such as “Mutual Funds Sahi Hai” for retail investor education.
- They proceed to identify who regulates mutual funds in India and the advantages of systematic investment.
- The Mutual Fund Industry in India is Regulated by SEBI to preserve public awareness and financial literacy.
The Role of SEBI in New Product Approvals
-
- Screening and clearing new fund schemes and alternative investment products shall be provided by SEBI.
- An Indian mutual fund industry regulation by SEBI to avoid inappropriate or overly complex products.
- Restraining regulatory arbitrage and making provisions for investor suitability.
SEBI and Digital Platforms
-
- SEBI oversees robo-advisory, online platforms, and AMFI-approved distributors like VSRK Capital.
- The Mutual Fund Industry in India is regulated by SEBI aims to impose cybersecurity and the appropriate use of investor data.
- Achievement of metadata protection and digital compliance norms.
FAQs
Who regulates the mutual funds in India?
As the primary regulatory authority, SEBI is responsible for overseeing every aspect of mutual fund functioning across India.
Why is the mutual fund industry in India is regulated by SEBI?
For protecting investors, ensuring transparency, and practicing sound business procedure.
Can SEBI impose penalties on AMCs?
Yes. SEBI can impose fines, suspend schemes, or withdraw licenses on the grounds of non-compliance.
How does SEBI promote investor protection?
Through disclosure norms, redressal avenues, code of ethics, and suitability checks.
Where to learn more about SEBI’s regulations?
Visit VSRK Capital, visit our Contact Us page, or check our Google Business Profile.
Conclusion
Knowing who regulates the mutual funds of India assists every investor in making an informed choice. The Indian mutual fund industry is regulated by SEBI with an eye to providing transparency, credibility, and systematic growth. Join hands with VSRK Capital to navigate through India’s mutual fund scenery confidently.
Regulator of MutualFunds in India Regulator of Mutual Funds in India